Why there’s more to vetting investors than Net Worth
If you want to find and close investors for your independent film project, there’s a lot more to it than simply googling a person’s net worth. Here’s an explanation.
I live something of a public life, and as such I try to keep tabs on what comes up when people google my name. I generally do a thorough search on myself about once a month. A few months back I found a link from a site that specializes in estimating the Net Worth of celebrities and other people in the public eye. They estimated my net worth to be about 12 million dollars. As much as I’d like to tell you that’s true, it’s not. At least not yet. So here’s why you should be careful in trusting Net worth estimates.
Edit: This site has taken down that page, and while I thought I had screencaps, I don’t.
If you want me to invest in your movie, read this
I have a feeling posting something on my film services site that says I’m worth 12 million dollars is going to get some investment inquiries, so let’s get this out of the way before we continue.
I don’t personally invest in projects beyond recoupable distribution expenses. If I do early-stage fundraising for clients, it’s only AFTER I’ve worked with them and developed a working relationship with them. That being said, I get the distinct impression a lot of people just skim my articles. So I’m including a big button below that links to my official policy on investing in people’s projects who contact me cold via social media. Those who skim my articles probably won’t like it, but I have to find some way of dealing with the near-constant bombardment of investment inquiries. Click it, you might get a laugh.
In the rare cases I do act as a conduit for investment, equity investment is never the first money in. It’s often not the last money in, but it’s definitely not the first. If you’re looking for me to invest in your film, it’s probably not going to happen. I’m more likely to help you set up your investment documents.
Related: The 9 ways to finance an independent film.
Net Worth isn’t as important as you may think.
So getting back to the meat and potatoes of the article. Net Worth probably doesn’t mean as much as you may think. The way Net Worth is calculated is pretty simple, you list your assets and calculate a value (Home Equity, Stocks, Bonds, Other investments) , then you list your liabilities (Debt of all kinds) then you subtract the value of your debts from the value of your assets and you’ve got a net worth.
The important to realize about this is that the majority of the assets I listed above aren’t what investors would call liquid capital. That means that in most cases, only a small portion of your net worth is spendable. There are ways to liquidate such assets without selling them, but that generally requires some level of loan and implies interest. For a bit more on that, check out the blog below.
Related: One Simple Tool to Reopen Conversations with Investors
So let’s look at my net worth as an example. First off, I have no idea where they got the 12 million dollar number. Even by the most generous valuations of my assets, it’s off by at least 3-4X. But even going with that generous valuation of my assets, most of that would be tied up in equity between Guerrilla Rep Media and ProductionNext. There’s not a whole lot I can do with those assets to liquidate them. Even if I could, it’s unlikely I would as I don’t think the asset is completely mature, and selling off shares would be unlikely to help me. This is actually a pretty common problem for investors and High Net Worth Individuals (HNWIs) and it’s something you should be on the lookout for when you’re vetting your investors.
Related: 5 Steps to Vetting your investor
It’s Not Money until you can buy beer with it
I’m quoting someone, but I’m not sure who. But in essence, just because someone has a high net worth doesn’t mean that they’re going to be willing or even able to invest in your project. If someone derives their net worth from owning a couple of multi-family homes and drawing income as a landlord, then even if their net worth is several millions, their assets are tied up in real estate and harder to access than you might think.
The only metric that really matters when courting an investor is how much investable capital they have at their disposal, and that’s a very different metric than their net worth that’s harder to pin down.
Thanks for reading, if you enjoyed this blog, I’d recommend you check out my mailing list for monthly blog digests., a free investment deck template, a free e-book, white paper, and a whole lot more. Click the button below for more information.
3 Things Every New Film Investor NEEDS to know
It’s not just filmmakers who need to understand the business. Investors do too. Here are a few words of advice on the film industry for new investors from an executive producer.
I write a lot about the film business with filmmakers as a target audience. However, in my non-educational content job, I have to interface with film investors on a fairly regular basis. This blog is adapted from one such situation where a first-time film investor had a lot of impulses that might actually hurt their film. The response got rather lengthy, so I asked my client if he minded if I adapt it into a blog. The client didn’t mind at all, so now I can share the insights with him with significantly more people.
With that in mind, here are 3 things that every new film investor should know.
1. Films are not evergreen.
Once a film is more than a year past its initial release, it loses a significant portion of its perceived market value. Buyers just won’t touch it. You released the film this year, so you have a bit of time, but that time is not infinite. This means that negotiations around a minimum amount of money over time is not always productive, as it will likely be out of the highest actual period no matter what happens. Often, even if you get the rights back, the film will have been so heavily shopped no one will take a look at it anyway.
This is a mistake that a lot of filmmakers make. Unfortunately, you do not have all the time in the world to shop for your film. Eventually, you’ll want to make sure you get it out there, even if it’s at something of a loss. If you want longer, it’s unlikely that your prospects will get better.
Of course, I want to be clear that you shouldn’t take any old deal as soon as it’s offered. It’s just important to remember that barring some incredibly specific extenuating circumstances, your film won’t be worth as much next year as it is now. Your Also, if the distributor or sales agent is in clear breach, you should still try to get your rights back.
2. Generally, films take a few markets to make a cash upfront sale, and the pay chain is absurd.
It often takes a few in-person touchpoints before the sale is finalized. While I’m going to be pushing for a quick sale, sometimes it takes a while for the money to come through.
Further, you should remember that a lot of time it will take a while for those payments to trickle through to the producer. I’ve outlined the issue in detail in the blog below, but to give you an idea, an MG-oriented sale will likely have something like 10% due on signing, 40% due within 30-90 days from notice of delivery, and the remaining 50% due prior to release or within 30 days of release. Also, most SVOD sales in the US pay out a set amount of time after the beginning of the license period.
Related:The problems with the indie film distribution payment system.
3. No one likes dealing with inexperienced people with huge egos.
If you’re an accredited investor, you’ve probably dealt with this issue on the other end. You likely have money due to your own entrepreneurial endeavors, a high-paying position that likely required you to employ other people, an expansive portfolio of investments that may have required you to interface directly with other entrepreneurs, or some combination of the above.
While the primary goal of any film production should be to get all of your money back, the industry is incredibly specialized. Nobody likes being told how to run their business by someone without much experience in the driver’s seat of this highly specialized industry.
It’s important to remember that once you get to dealing with more powerful members of the industry, trying to throw your weight around to get a better deal isn’t likely to break in your favor. Unfortunately, most good sales agents or distributors will just decline to take out your film, and the less-than-good ones who remain will find legal ways to avoid paying out as long as possible if they pay out at all.
This industry may be in a period of upheaval, but currently, sales agents and distributors still hold a lot of power. So if you want to make a profitable film, or a widely distributed one, you’re going to have to take some time to understand the common industry practices.
It’s incredibly difficult to negotiate with someone when you’re at a massive informational disadvantage, and more than likely you will be at an informational disadvantage purely by the nature of the specialization of the film sales and distribution industry.
If you want to lessen your informational disadvantage, you should sign up for my mailing list to get monthly blog digests segmented by topic, you’ll also get a free film business resource pack that includes an ebook, whitepaper on the macroeconomics of the film industry, an investment deck template, and a whole lot more! Click the button below to grab it.
Check out the tags below for related content.
Filmmakers Glossary of Film Investment Terminology
It’s hard to raise funding for a film, and the contracts get confusing quickly. Here’s a glossary to help you understand the mountain of paperwork you’ll need to sign to get your film financed. This blog doesn’t mean you don’t still need a lawyer (I’m not one, and this isn’t legal advice), but it will help you understand the paperwork you’re sent.
Last week I laid out a glossary of general-use film business terms, but the blog ended up a bit too long and dense to be a single post. So, I broke it into two. Last week was the basics of business terms, this week is the next level, and focuses entirely on investment terms. Some of these may seem tangential and unnecessary, however if your goal is to close an investor, you’ll need to thoroughly speak their language. If there’s something you don’t see here, check out last week’s blog here. I’m not a lawyer, this isn’t legal advice, and you should have a solid attorney on your team before trying to close an investment round. With that out of the way, let’s get started.
Capital
While many types exist, The term most commonly refers to money.
Liquid Capital
Money that can be spent immediately, or near immediately. Non-liquid capital would be considered something like real estate holdings which would first need to be liquidated in order to sell.
Principle
In finance: it’s general the initial capital investment or the remaining balance on a debt.
Interest
A percentage fee is added on to the principle of a loan or line of credit.
Compound interest
Interest on the principle of the loan and interest.
Simply: interest on interest.
High-Risk Investment
An investment where an investor may lose most or all of the money they put in. Independent Films are always high-risk investments
Securities and Exchanges Commission (SEC)
The main financial regulatory agency in the United States. It oversees most forms of investment.
Accredited Investor
A person of means who is generally considered to have enough business know-how to appraise an investment, pay someone to appraise it for them, or who wouldn’t be completely destitute from taking a high risk-gamble. As of the date of this publishing, according to the SEC the investor must meet either (NOT both of) the income or net worth requirement in order to be considered an accredited investor.
Income Requirements
1.If filing individually, a person must have made 200,000 USD a year for the past 2 years, and be likely to do the same this year.
2.If filing Jointly, a household must have made 300,000 USD a year for the past 2 years, and be likely to do the same this year.
Net Worth.
The investor or household must have 1 million dollars in net worth OUTSIDE of their primary residence.
High Net Worth Individual (HNWI)
Outside the obvious, this term is generally a financial industry term for accredited investor
Edgar Database
A database of high-risk investments maintained by the SEC that is only accessible to Accredited investors and licensed brokerage or investment firms.
Financing Round
A round of financing or funding that is large enough to take an organization or project to the next major milestone. For how this works in film, check out the youtube video I’ve linked below, and the blog linked below that.
Related Video: The 4 Stages of Indiefilm Financing
Related Blog: The 4 Stages of Indiefilm Financing
Business Plan
A document written by an entrepreneur or filmmaker outlining their investment. In the film industry, this document will also often educate the investor on how the industry functions as a whole. This document is also known as a prospectus, but that term is not as commonly used as it once was.
Private Placement Memorandum (PPM)
A document that’s filed with the SEC for investors to consider investing in your project. Frequently an attorney will base this document off of the filmmaker or entrepreneur’s business plan. In most cases, a PPM will be registered with the aforementioned Edgar database for a modest filing fee.
Pro-Forma Financial Statements
Financial documents consisting of an expected income breakdown, cash-flow statement, and top sheet budget to be invaded in the business plan and function as the basis for many of the financial sections of other documents
The Three points above are heavily outlined in my business planning blog series.
Related: How to write an independent Film Business Plan (1/7)
Backed Debt
A secured loan backed by something like a tax incentive or pre-sale agreement.
Unbacked Debt
An unsecured loan, or debt without backing. Generally very high interest.
Financial Gap
The space between what you are able to raise and the amount you need to finish your project.
Financial Markets
A market where stocks, bonds, derivatives, or other securities are bought and sold. Common examples in the US would be the DOW and the NASDAQ.
Film Market
A convention where films are bought and sold primarily by sales agents and distributors. For more, check out the link below.
Related: What is a film market and how does it work?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all newly finished goods in a given country during a set timespan. Most commonly calculated on an annual basis.
Recession
A macroeconomic term signifying a period of a significant decline in economic activity. It’s generally only recognized after two consecutive quarters of down financial markets.
Depression
A severe recession that lasts longer than 3 years and corresponds with a drop in GDP of at least 10%
Bull Market
A market that’s strong and growing. It’s called a bull market as the upward trending graph looks like a bull nodding its head according to some people on Wall Street.
Bear Market
Yes, I spelled that right. It’s a financial market that’s going down, or staying stagnant. The name comes from a bear swiping its claws down. Probably the same wall street guy came up with it.
Thanks so much for reading! If you liked this, please make sure to check out last week’s general financing glossary, as well as my glossary of distribution terms. Also, please share. It helps A LOT.
Filmmakers Glossary of Business Terms
Additionally, make sure you grab my free Film Business Resource Package to get a print ready PDF version of all 3 glossaries.
Check the tags below for more related content.
Filmmakers Glossary of Film Business Terminology.
I’m not a lawyer, but I know contracts can be dense, confusing, and full of highly specific terms of art. With that in mind, here’s a glossary of Art. Here’s a glossary to help you out.
A colleague of mine asked me if I had a glossary on film financing terms in the same way I wrote one for film distribution (which you can check out here.) Since I didn’t have one, I thought I’d write one. After I wrote it, it was too long for a single post, so now it’s two. This one is on general terms, next week we’ll talk about film investment terms. As part of the website port, I’m re-titling the first part to a general film business glossary of terms, to lower confusion on sharing it. It’s got the same terms and the same URL, just a different title.
Capital
While many types exist, it most commonly refers to money.
Financing
Financing is the act of providing funds to grow or create a business or particular part of a business. Financing is more commonly used when referring to for-profit enterprises, although it can be used in both for profit and non-profit enterprises.
Funding
Funding is money provided to a business or non-profit for a particular purpose. While both for-profit and non-profit organizations can use the term, it’s more commonly used in non-profit media that the term financing is.
Revenue
Money that comes into an organization from providing shrives or selling/licensing goods. Money from Distribution is revenue, whereas money from investors is financing, and donors tend to provide funding more than financing, although both terms could apply.
Equity
A percentage ownership in a company, project, or asset. While it’s generally best to make sure all equity investors are paid back, so long as you’ve acted truthfully and fulfilled all your obligations it’s generally not something that you will forfeit your house over. Stocks are the most common form of equity, although films tend not to be able to issue stocks for complicated regulatory reasons and the fact that films are generally considered a high-risk investment.
Donation
Money that is given in support of an organization, project, or cause without the expectation of repayment or an ownership stake in the organization. Perks or gifts may be an obligation of the arrangement.
Debt
A loan that must be paid back. Generally with interest.
Deferral
A payment put off to the future. Deferrals generally have a trigger as to when the payment will be due.
“Soft Money"
In General, this refers to money you don’t have to pay back, or sometimes money paid back by design. In the world of independent film, it’s most commonly used for donations and deferrals, tax incentives, and occasionally product placement. It can have other meanings depending on the context though.
Investor
Someone who has provided funding to your company, generally in the form of liquid capital (or money.)
Stakeholder
Someone with a significant stake in the outcome of an organization or project. These can be investors, distributors, recognizable name talent, or high-level crew.
Donor
Someone who has donated to your cause, project, or organization.
Patron
Similar to donors, and can refer to high-level donors or financial backers on the website Patreon. For examples of patrons, see below. you can be a patron for me and support the creation of content just like this by clicking below.
Non-Profit Organizations (NPO)
An organization dedicated to providing a good or service to a particular cause without the intent to profit from their actions, in the same way, a small business or corporation would. This designation often comes with significant tax benefits in the United States.
501c3
The most common type of non-profit entity file is to take advantage of non-profit tax exempt status in the US.
Non-Government Organization (NGO)
Similar to a non-profit, generally larger in scope. Also, something of an antiquated term.
Foundation
An organization providing funding to causes, organizations and projects without a promise of repayment or ownership. Generally, these organizations will only provide funding to non profit organizations. Exceptions exist.
Grantor
An organization that funds other organizations and projects in the form of grants. Generally, these organizations are also foundations, but not necessarily.
Fiscal Sponsorship
A process through which a for-profit organization can fundraise with the same tax-exempt status as a 501c3. In broad strokes, an accredited 501c3 takes in money on behalf of a for-profit company and then pays that money out less a fee. Not all 501c3 organizations can act as a fiscal sponsor.
Investment
Capital that has been or will be contributed to an organization in exchange for an equity stake, although it can also be structured as debt or promissory note.
Investment Deck (Often simply “Deck”)
A document providing a snapshot of the business of your project. I recommend a 12-slide version, which can be found outlined in this blog or made from a template in the resources section of my site, linked below.
Related: Free Film Business Resource Package
Look Book
A creative snapshot of your project with a bit of business in it as well. NOT THE SAME AS A DECK. There isn’t as much structure to this. Check out the blog on that one below.
Related: How to make a look book
Audience Analysis
One of 3 generally expected ways to project revenue for a film. This one is based around understanding the spending power of your audience and creating a market share analysis based on that. I don’t yet have a blog on this one, but I will be dropping two videos about it later this month on my youtube channel. Subscribe so you don’t miss them.
Competitive Analysis
One of 3 ways to project revenue for an independent film. This method involves taking 20 films of a similar genre, attachments, and Intellectual property status and doing a lot of math to get the estimates you need.
Sales Agency Estimates
One of 3 ways to project revenue for an independent film. These are high and low estimates given to you by a sales agent. They are often inflated.
Related: How to project Revenue for your Independent Film
Calendar Year
12 months beginning January 1 and ending December 31. What we generally think of as, you know, a year.
Fiscal year
The year observed by businesses. While each organization can specify its fiscal year, the term generally means October 1 to September 30 as that’s what many government organizations and large banks use. Many educational institutions tie their fiscal year to the school year, and most small businesses have their fiscal year match the calendar year as it’s easier to keep up with on limited staff.
Film Distribution
The act of making a film available to the end user in a given territory or platform.
International Sales
The act of selling a film to distributors around the world.
Related: What's the difference between a sales agent and distributor?
Bonus! Some common general use Acronyms
YOY
Year over Year. Commonly used in metrics for tracking marketing engagement or financial performance on a year-to-year basis.
YTD
Year to Date. Commonly used in conjunction with Year over year metrics or to measure other things like revenue or profit/loss metrics.
MTD
Month to Date. Commonly used when comparing monthly revenue to measure sales performance. Due to the standard reporting cycles for distributors, you probably won’t see this much unless you self-distribute.
OOO
Out of Office. It generally means the person can’t currently be reached.
EOD
End of Day. Refers to the close of business that day, and generally means 5 PM on that particular day for whatever the time zone of the person using the term is working in.
Thanks for reading this! Please share it with your friends. If you want more content on film financing, packaging, marketing, distribution, entrepreneurialism, and all facets of the film industry, sign up for my mailing list! Not only will you get monthly content digests segmented by topic, but you’ll get a package of other resources to take you film from script to screen. Those resources include a free ebook, whitepaper, investment deck template, and more!
Check the tags below for more related content!
What Every Investor Needs to Know about Your Independent Film
If you want to raise money for your independent Film, Here are a few things your investor will need to know.
They say that most people know whether or not they would get into bed with someone in the first conversation. Admit it, you didn’t realize I was talking about investors giving you money right there, did you? Jokes aside, there are a few key things your investor is going to need to know about your project in order to give you any serious consideration.
But before we get started, let me clarify that this is not the entire conversation. This Is the conversation that will get you to the point you can send over documents for much deeper consideration. Also, any one of these key points can disqualify an investor or a distributor. That doesn’t necessarily mean it’s bad, it just means it’s not for them
Related blogs: How to Write a Look Book, Deck, & Business Plan (series)
Stage of development
There’s more than one time you’ll need to raise money. As such, it’s good to clarify where you are with it upfront.
Related: The 4 Stages of indiefilm Financing (and where to find the money)
Genre
Your film is hugely important. Generally, you’ll want to only list one genre as it denotes the style and feel of your film, and maybe 2-3 sub genres as those will inform both your setting, your audience, and general themes. An example would be Goodland is a Slow-Burn Crime Thriller.
Related: Why Genre is VITAL to Indiefilm Marketing & Distribution
Related: How Distributors Think of Genre & Sub Genre
Attachments
Investors will want to know who you have on board. This can be distributors, recognizable name talent, tested directors, or anything else that may be marketable. A couple of examples would be Black Gold: America is Still the place stars Mike Colter (AKA Marvel’s Luke Cage.) It could also be The Cutlass has Wild Eye Releasing attached for Domestic distribution, and Leomark Studios handling international Sales.
Related: Why your film still needs recognizable name talent.
Budget
If you’re talking to an investor, you should say your total budget. If you’re talking publicly to a distributor, you should give a range. An example would be Goodland is a SAG Ultra-Low Budget Small town Crime thriller if you’re talking to anyone other than an investor. If you’re talking to an investor, you’d say Made Up Movie Name is budgeted at 17 million dollars and we already have Governator McActionFace attached to star in it. That’s why we need the extra 10 million beyond the 7 we already raised.
Logline
Your logline isn’t a 20 page treatment. It’s a punchy sentence describing your project. Everything up to this point is something you should be able to get out in about 10-15 seconds.
An example would be Goodland is a Completed SAG-AFTRA Ultra Low Budget Crime Thriller set in rural Kansas. When a mysterious photographer shows up in town the same day the body of a drifter turns up dead in a cornfield, the local sheriff (played by Cinnamon Schultz of Winter’s Bone) must piece together the conspiracy before it’s too late.
Financial Mix
The big reason your investor needs to know this is to make a better risk assessment. It will also inform how much you’re asking them for. You should never expect investors to cover your whole budget.
An example of this would be something like Of our 4 million dollar budget, we’re raising 2.5mm in equity. The rest is being covered by an MG-backed Presale from our sales agent, tax incentives from that place we’re shooting are being monetized by huge state businesses.
(Author's) note: Since it came up in the comments, I thought I'd clarify that the 4 million dollar example above is taken from a different film as the one I mentioned in the logline example.
Read more: The 9 ways to finance an independent film
Related: What’s the difference between an LOI & a Presale?
Target Demographic/Expected Audience
Your Investor is going to want to understand how they get you’re going to get their money back to them, which means that you need to know who will buy your movie. Think of this as placing a target, so you know where to shoot the arrow in the next step. An example would be: After a few test screenings, we’ve realized that the target audience for The Cutlass is women aged 30-49. Or, Based on ratings data gathered from similar films on IMDb Pro, we expect that that Made-up-action-movie starring Governator McActionFace will appeal primarily to Non-college educated White Men aged 30-55. Especially those in Texas.
Related: How do I figure out who to sell my movie to?
Marketing Plan.
Finally, they’ll need to know how you plan to reach that audience. If figuring out your audience is placing the target, Marketing is shooting the arrow.
As an Example: The Cutlass will be available across all standard TVOD platforms, Amazon Prime, and SVOD platforms. We’ll utilize an aggressive PR and Awareness campaign to reach our core demographic, and get seeded in Amazon Prime’s Algorithm, and we will consider additional artwork to appeal to our new demographic.
Another example, Made-Up-Action Movie will utilize Governator McActionFace’s star power to raise awareness on the standard talk-show circuit prior to the US Release, while seeding early adopters with press and advance screenings in Texas, Montana, parts of Colorado, and Arizona. Our theatrical run will focus primarily on screens in smaller secondary and rural markets.
Thanks so much for reading! If you liked this blog, and want more like it, share it on your social media.
Blogging might look like my full-time job, but it’s not, I also distribute and consult on movies. Some of which I listed above. If you’d like yours to be next, click the relevant button below. If you want to stay up to date about classes, events, and other filmmaker focus content, as well as get a resource packet with lots of valuable templates and other exclusive resources, join my mailing list with the button below.
The Problem with the IndieFilm Distribution Payment System
If you’ve got an issue with your sales agent or distributor paying you, it’s not neccessarily on them. (although it might well be.) either way, Its important to understand how money flows in this industry before you go at them.
A lot of filmmakers I’ve worked with don’t know enough about distribution to really make a career making creative content. This shouldn’t be a surprise, as it’s something film schools tend not to teach. That being said, there’s a part of the equation most people just don’t talk about, and WHY it takes so long for filmmakers to get paid? This blog addresses that.
As an aside, this is laid out from a financial perspective in the blog below. However, we will also be tracking how much of the money goes away throughout this blog. This will admittedly be very much oversimplified, but we’re going to be tracking it as a single dollar for ease of understanding.
Related: Indiefilm Waterfalls 101
How long it takes for the platform to pay the aggregator
I talk about this in workshops quite frequently, but each different stakeholder takes a while to pay the next person in the pay chain. Most of the time, this starts with the platform and aggregator relationship. In general, this is the first section in the chain.
Normally, the platform will take 30%-35%. This should include credit card processing fees. So if the consumer gave 1 dollar, then we’re down to 65-70 cents.
While exceptions exist, the platform most often pays the aggregator on a monthly basis. After that, the aggregator will need to pay the distributor. If you’re self-distributing, that distributor is you, but not all aggregators will deal with you in the fashion you’d prefer, for more information, read the blog below.
RELATED: What platforms should I release on?
How long it takes for the aggregator to pay the distributor
Once the aggregator is paid, the money will flow to the distributor. As I stated, this may be you. Depending on what aggregator the distributor is using, payments will be either monthly or quarterly. Sometimes the aggregators that pay quarterly have lower overheads, so it might make sense to wait. That said, I think the most current data you can get is necessary to make smart marketing decisions.
If you still don’t know the difference between a sales agent and a distributor, check the link below. Most aggregators operate on more of a flat fee model, so we’ll assume that the money is passed through. If you worked with an aggregator, you end up with about .70 cents for every dollar the consumer spent, but you also probably had to put the aggregation fees in yourself, so you’ll probably need to sell around 2100 copies (assuming they sell for 2.99 each) to break even. You’ll also get insights within 2 to 4 months.
Related: What’s the difference between a sales agent and a distributor?
How long it takes for the Distributor to pay the Sales Agent
Most distributors don’t deal with filmmakers directly. They’ll either deal with a Producer’s Rep or a Sales Agent. Generally, Distributors pay quarterly to start and sometimes will move more towards bi-annually after a few years. This can be arduous, but it’s very difficult to negotiate.
Generally, the distributor will take 30-40%. (As of publishing this, I take 25% for direct US Distribution.) So of the 65-70 cents, we had after the platform. That means that after the distributor takes their cut, there are between .39 and .49 cents left to the filmmaker. (or around .52 cents if you work with me)
Also, even though I am a distributor, I work directly with filmmakers. So you’d keep .52 cents on the dollar, and be paid around 4-5 months after the initial sale is made. (I time my reports to work with my aggregator to minimize wait times. Plus, I cover aggregation and the majority of marketing and publicity fees.
Related: What does a producer’s rep do anyway?
How long it takes for the Sales agent to pay the production company
Finally, the sales agent pays the Producer’s Rep and production company. This is also generally on a quarterly or Bi-Annual basis, although there’s more room for variation here. After that, the filmmaker uses the money to pay back debts, then investors, then whoever else is left to pay back from the production.
The Sales Agent normally takes between 20% and 30%, but they sell territories across the globe. A Producer’s Rep will normally take 10% of the money paid to the filmmaker, and will normally be paid in line with the sales agent.
So, following the chain we talked about before, by the time the sales agent pays the filmmaker, we’re looking at between .27 and .39 cents on the dollar without a producer’s rep, or between .24 cents and .35 cents with one. That’s not a great representation of what a good producer’s rep will do for you though. (including the potential to get you paid immediately from the first sale) I’ve painted these deals in the most simple possible light to help you understand, but there are lots of single-line items that can screw you if you’re not careful. So, while the producer’s rep may take a small piece of the pie, (.03 to .04 cents on the total dollar) they can help you make the whole pie a fair amount bigger.
Thanks so much for reading! If you have any questions for me, you might want to check out my mailing list. I send out monthly blog digests including ones JUST LIKE THIS, plus you get lots of great resources like templates, links to money-saving resources, and a whole lot more! Or, if you’ve got a completed project and you’re looking for distribution, submit it using the link below. You can also learn more about services for early-stage projects using the other link. I’ll review it and reach out soon.
Check out the tags below for more related content!
When and Where to use Each Indiefilm Investment Document
Most Sales agents don’t want your business plan, and a bank doesn’t want your lookbook. Here’s what stakeholders do want, and when.
There are 3 different documents you would need to approach an investor about your independent film. I’ve written guides on this blog to show you how to write each and every one of them. Those three documents are a Look Book (Guide linked here.) a Deck (Guide Linked Here) and a business plan. (Part 1/7 here) But while I’ve Written about HOW to create all of these documents, I’ve held back WHY you write them, WHO needs them, and WHEN to use them. So this blog will tell you WHO needs WHAT document WHEN and HOW they’re going to use it.
As with some other blogs, I’ll be using the term stakeholder to refer to anyone you may share documents with, be they an investor, studio head, sales agent, Producer of Marketing and Distribution (PMD) or Distributor.
What are these documents and WHY do you share them?
So first, let’s start with what each document is, just in case you haven’t read the other blogs (which you still should)
A Look book for an independent film is an introductory document, that’s very pretty and engaging and gives an idea of the creative vision of the film. The purpose is to get potential stakeholders interested enough in the project to request either a meeting or a deck. The goal in showing them this document is to get them to start to see the film in their head and get them to become interested in the project on an emotional level.
Related: Check out this blog for what goes into a lookbook
A Deck is a snapshot of the business side of your film. The goal is to send them something that they can review quickly to get an idea of how this project will go to market and how it will make money so that they get an idea of how they’ll get their money back.
Related: The 12 Slides you need in your indie film investment Deck
A business plan is a detailed 18-24 page document broken into 7 sections that will give potential investors not only an idea of your investment but of the industry as a whole. In a sense, it’s equal parts education and persuasion, especially for investors new to the film industry. The goal is to give the prospective stakeholder a deeper understanding of the film and media industry, and a very thorough understanding of your project and the potential for investing in it.
Related: How to Write an Indiefilm Business Plan (1/7 - Executive Summary)
WHO needs these documents and HOW they’ll use it
Different stakeholders need these documents at different times.
Look Books should be sent to any potential stakeholder, including investors, studio heads, sales agents, distributors, producer’s reps, Executive Producers, and more. It’s a creative document that gives a good idea of the product at the early stage. It helps people gauge interest in your project
Decks are primarily used by Investors, Executive Producers, PMDs, and potentially Sales Agents. Distributors and Studio Heads are less likely to need a deck since they know the business better than you do. At least most of the time.
Business plans are primarily needed by angel investors new to the film industry and Angel Investment Syndicates to use as the backbone for the Private Placement Memorandum (PPM) The First and last sections of the business plan (The Executive Summary and Pro-Forma Financial Statements) may be more widely used, often at the same general place as the deck, or only shortly after.
WHEN do they need these documents?
Look books come early on. It’s generally the first thing they’ll ask for when considering your project.
Decks come shortly after the lookbook. Sometimes in an initial meeting, or sometimes directly after that first meeting.
Looking at a business plan is generally very deep in the process of talking to a potential stakeholder, it’s almost always after at least 2-3 meetings and a thorough review of the deck.
If this was useful, you should definitely grab my free film business resource packet. It’s got templates for some of these documents, a free e-book, a whitepaper that will help you write these documents, as well as monthly blog digests segmented by topics about the film business so you can sound informed when you talk to investors. Click the button below to grab it right now.
Check out the tags for related content.
How to Make LookBook for an Independent Film
Decks and lookbooks are not the same. Here’s how you make the latter.
I’ve written previously about what goes into an indie film deck, but as I get more and more submissions from filmmakers, I’m realizing that most of them don’t fully understand the difference between a lookbook and a deck. So, I thought I would outline what goes into a lookbook, and then I’ll come back in a future post to outline when you need a lookbook when you need a deck, and when you need a business plan.
What goes in a lookbook is less rigid than what goes in a deck. It’s also designed to be a more creatively oriented document than a deck. But in general, these are the pieces of information you’ll need in your lookbook. I’ve grouped them into 4 general sections to give you a bit more of a guideline.
You’ll often see the term stakeholder. I use this to mean anyone who might hold a stake in the outcome of your project, be they investors, distributors, or even other high-level crew.
Basic Project Information
This section is to give a general outline of the project and includes the following pieces of information.
Title
Logline
Synopsis
Character Descriptions
Filmmaker/Team bios
The title should be self-explanatory, but if you have a fancy font treatment or temp poster, this would be a good place to use it.
The logline should be 1 or 2 sentences at most. It should tell what your story is about in an engaging way to make people want to see the movie. You probably want to include the genre here as well,
The synopsis in the lookbook should be 5-8 sentences, and cover the majority of the film’s story. This isn’t script coverage or a treatment. It’s a taste to get your potential investors or other stakeholders to want more.
Character descriptions should be short, but more interesting than basic demographics. Give them an heir of mystery, but enough of an idea that the reader can picture them in their head. Try something like this. Matt (white, male, early 20s) is a bit of a rebel and a pizza delivery boy. He’s a bit messy, but nowhere near as bad as his apartment. He’s more handsome than his unkempt appearance lets on, If he cleaned up he’d never have to sleep alone. But one day he delivers pizza to the wrong house and gets thrust into time-traveling international intrigue.
Even that’s a little long, but I wasn’t actually basing it on a movie, so tying it into the film itself was trickier than I thought it would be. That would be alright for a protagonist, but too long for anyone else.
Filmmaker and Team bios should be short, bullet points are good, list achievements and awards to put a practical emphasis on what they bring to the table DO NOT pad your bio out to 5000 words of not a lot of information. Schooling doesn’t matter a lot unless you went to UCLA, USC, NYU or an Ivy League school.
Creative Swatches
These are general creative things to give a give the prospective stakeholder an idea of the creative feel of the film. They can include the following, although not all are necessary.
Inspiration
Creatively Similar Films
Images Denoting the General Feel of the Film
Color Palette
The inspiration would be a little bit of information on what gave you the vision for this film. It shouldn’t be long, but it definitely shouldn’t be something along the lines of “I’ m the most vissionnarry film in the WORLD. U WILL C MAI NAME IN LAIGHTS!” (Misspellings intentional) Check your ego here, but talk about the creative vision you had that inspired you to make the film. Try to keep it to 3-4 sentences.
Creatively similar films are films that have the same feel as your film. You’re less restricted by budget level and year created here than you would be in a comp analysis, that said, don’t put the Avengers or other effects-heavy films here if you’re making an ultra-low budget piece. I’d say pick 5, and use the posters.
Images denoting the general feel of the film are just a collection of images that will give potential stakeholders an idea of the feel of the film. These can be reference images from other films, pieces of art, or anything that conveys the artistic vision in your head. This is not a widely distributed document, so the copyright situation gets a bit fuzzy regarding what you an use. That said, the stricter legal definition is probably that you can’t use without permission. #NotALawyer
The color palette would be what general color palette of the project. This is one you could leave out, but if there’s a very well-defined color feel of the film like say, Minority Report, then showing the colors you’ll be using isn’t a terrible call, Also,, it's generally best to just let this pallet exist on the background of the document on your look book.
Technical/ Practical swatches
This section is a good indicator of what you already have, as well as some more technical information about the film in general. It should include the following.
Locations You’d like to shoot at
Cities You’d Like to shoot in
Equipment you plan on using
Photos are great here, if you use cities or states include the tax incentives for them, The equipment should only be used if it’s the higher end like an Arri or Red. If you’re getting it at a fantastic cost, you should mention that here as well. People tend not to care about the equipment you’re using, but if you’re going to put it in any pitch document, this is the one.
Light Business Information
The lookbook is primarily a creative document, but since most of the potential stakeholders you’re going to be showing it to are business people, you should include the basics. When they want more, send them a deck.
Here’s what you should include
Ideal Cast list & Photos
Ideal Director List
Ideal Distributors
These are important to assess the viability of the project from a distribution standpoint. It can also affect different ways to finance your film. If your director is attached, don’t include that. If you have an LOI from a distributor, don’t mention potential distributors. Unless your film is under 50k, don’t say you won’t seek name talent for a supporting role. You should consider it if it’s even remotely viable.
If this was useful to you but you need more, you should snag my FREE indiefilm resource package. I’ve got lots of great templates you get when you join, and you also get a monthly blog digest segmented by topic to make sure you’re informed when you start talking to investors. Click below to get it.
How do we Get More Investors into Independent Film?
How do we get more investors in the film industry? We improve the viability of film as an asset class. Here’s how.
Throughout writing this blog series, I’ve been told more times than I can count that film is a terrible investment, and no one besides hobbyists would consider it. Many want to leave it there, without bothering to look at what’s causing it. Last week we thoroughly examined the issues plaguing the film industry, and what keeps investors out. The issues aren’t pretty, but they may be fixable. What follows is a list of what could be done to fix this problem and some of the ways organizations that are implementing these tactics.
Greater Transparency
One of the biggest things stopping film investment is the perception that it’s unprofitable. All too often that’s not simply a perception. Another thing stopping independent film as an industry from being profitable is the fact that many sales agents don’t accurately report the earnings of the films they represent. Others charge too much in recoupable expenses, so it’s unlikely to recoup. Some take an unreasonable portion of the revenue or simply hide sales from filmmakers.
One necessary problem to fix is the lack of transparency within distribution. There are rights marketplace solutions like Vuulr and RightsTrade emerging thanks to recent technologies for international distribution. Aggregators like BitMax and FilmHub have been around for a while already. The issue that these platforms have yet to solve is that of both audience and industry awareness of their project. If a filmmaker can market or receive help with that audience discover and marketing, then in theory the entire process can be disintermediated and filmmakers can sell directly to customers using a marketplace. Unfortunately, this discovery issue is still both time-consuming and expensive.
What about a hybrid system? One where a skilled group works with distributors and sales agents to sell the completed films at the maximum possible profit to the investors and production company. What if those groups were directly linked to protecting the investor’s interests, and gives sales agents capital for growth and new projects? Then the sales agents would have much better incentives to ensure the companies that license their content to them get a strong return.
That would seem like a solution, but we’ll get to it. There are other problems to delve into first.
Better Business Education for Filmmakers.
I touched on this in my last blog, but filmmakers don’t understand the business well enough to function as media entrepreneurs. Traditionally, specialists such as executive producers, PMDs, and true producers focused on the marketing and supported projects so that the writers, directors, creative producers, and line producers could focus on making the project. With film sets getting leaner, there aren’t enough of media entrepreneurs doing their jobs. (although I take on this role from time to time.)
In essence, there isn’t enough of a skilled entrepreneur class capable of making and selling films as a product either directly to consumers or to distributors, sales agents, and other industry outlets. So long as filmmakers don’t understand business, they’ll never be able to break out and get what they and their films are worth. If filmmakers don’t endeavor to understand business, they will be unable to communicate with investors and understand where they come from well enough to make a sustainable living in film. This issue is exacerbated by the fact that film schools don’t teach any of these skills as well as they should.
Filmmakers want to make the movie, and they will stop at nothing to get that done. As a result, promoting the film becomes an afterthought far too often. What would be ideal is if these educational organizations could tie into an angel investment group or community.
But what about integrating with an investor class and/or investment group?
Educated Investor Class
Investors generally understand business, but the film industry is ripe with its own nuances and idiosyncrasies. Investors need to know how money flows from them to create the product, then to take the product to market through various forms of distribution, and how that money eventually gets back to that same investor. Investors need tools to tell when someone is offering a con instead of an investment. It’s not the easiest thing to find information on, and when they do it’s focused more on the filmmaker than the investor.
If an investor doesn’t understand the issues within the film industry, then it’s less likely they’ll be able to properly vet an investment. If that same school that teaches filmmakers business, could teach investors about the nuances involved in the film industry, then there could be something of a connection point at a different sort of event.
Curators and tastemakers with Access to MEANINGFUL Distribution.
Just because an investor knows about how money comes in and out of the film industry doesn’t mean they can find quality films in which to invest. Being a professional Investor is all about quality deal flow. Indiefilm success tends to make less money than a successful technology startup, so curation and guidance is even more important.
Sure, nobody knows everything, but a curated eye can help separate the wheat from the chaff. Most investors don’t have a trusted source to review projects for feasibility and potential returns. Investment is about more than just money. Investors often act as business advisors. Unfortunately, not enough angel investors understand the industry well enough to do that effectively. However, if the curation board also acted as advisors on the projects, then the potential returns get much higher.
As an example, if that board had access to distribution, then you could cut out the biggest risk of investing in film. A member of the curation board could get the films to the proper PayTV, TVOD, SVOD and other distributors to help the fund managers.
A way of Discovering new talent
It’s always been a problem to find the next Quinten Tarantino, Jennifer Lawrence, or Jason Blum. Everyone has heard stories of how everyone in Hollywood is related. While it's more true than anyone wants to admit, the on set path to grow your career has become more difficult and less sustainable than it once was.
It's not an easy problem to solve. It’s difficult to tell the difference between that person who’s DEFINITELY going to be the next big thing but ends up washing cars two years later and the dweeby 20 year old who no one thinks will ever make anything of themselves makes millions at the box office on their directorial debut. This problem may be the most difficult of any listed.
Making your first film is incredibly difficult. It’s also very difficult to get it financed. From an investor perspective, they put in all the money up front ant they’re the last to be paid. It’s incredibly high risk with little reward.
Marketing a film is also quite difficult, and generally involves additional expenditure when the coffers are dry. This has killed many films before they saw the light of day. If a fund were to offer finishing funds to new filmmakers, they keep their risk incredibly low while opening up new discovery options.
Sure, it doesn’t help get the film made in the first place, but it can help get it finished and out there. The barrier to entry of having a nearly completed film also cuts down on the pool of potential applicants in a way that necessitates them showing they have the mettle to actually make something. That fund could also give preference to successful filmmakers for their second, third, and fourth projects. Such a system could enable a fund to retain the quality people they need to make a successful organization, while still opening the ranks for discovery.
Staged Financing
Investment in film is inherently speculative an as a result incredibly high risk. But the risk could be made lower by borrowing some techniques from Silicon Valley VCs. Instead of funding 100% of a film upfront in equity, an investor could stage their investment over the course of the film, at key points where the filmmakers would require more money.
It’s not something that could be done with a simple line in the sand due to the difficulty in getting recognizable name talent on board the project, but there are systems that could be used to mitigate risk while maintaining the ability to make high-quality name-driven projects that have a higher chance of financial success than directorial debuts with no names attached. It’s not a magic bullet, but it could mitigate the problem enough for other solutions to be more possible.
Staged financing would make it much more approachable for investors, since the risk to the individual investor is significantly smaller. But there are ways an organization could further limit the risk. How you ask?
Same Funder Providing different securities.
As mentioned in part 6 of this series, equity investors are the last to be paid on most projects due to where they fall in the waterfall in relation to Platforms, Distributors, Sales Agents, and the like. This is due in part to filmmakers needing to secure debt-backed securities from different funders in order to complete the project. These debt-backed securities must be paid before the investors are, which further disincentives the equity investment from the original investors.
But what if the different securities were made available from the same group? That way a fund could offer the same pool of investors the last in first out debt in order to protect the interest in their equity position. From my vantage, that would seem to protect both the investor and the filmmaker by enabling the investor to mitigate risk and the filmmaker to maintain greater ownership of their projects, and a higher profit share once the debt is paid off.
Thanks for reading. This one required A LOT of rewriting as part of the archive transfer/website port. If you made it this far, you should sign up for my email list to get my free film business resource pack. You’ll get blogs just like this one segmented by topic, as well as a free e-book, investment deck template, contact tracking templates, form letters, and more!
Check out the tags below for more related content!
6 Things stopping a sustainable investor class in film.
If you’ve ever raised money to make a film, you know it’s hard. It’s not because individual films can’t be good investments, it’s that the problems with the industry are systemic. Here’s a look at why.
Much of this series has been focused on the numbers behind film investment. While metrics like ROI and APR are very important when considering an investment, they’re not the only reason that high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) tend to shy away the film industry. Here are 6 things that are stopping them.
In order for independent film to develop a sustainable investor class, the asset class itself needs to be taken more seriously. The reason that no one has yet been able to create a sustainable asset class out of film and media is much more complicated than the numbers not being in our favor. In this post, we’re going to examine some of the other things stopping independent film from becoming a sustainable asset class. This list is in no particular order, except how it flows best.
1. LACK OF INVESTOR EDUCATION
Investors tend not to invest in things they don’t know or understand, at least as anything more than an ego play. The Economics behind film investment is difficult to understand even before you factor in how difficult it is to find reliable information on film finance from an investor’s perspective.
Even the basics of the industry can be difficult to learn. Generally, film investors are forced to read older, often out-of-date books on film financing targeted more at filmmakers than at investors. This industry is in the midst of a reformation, so much of the information is out of date before it’s published. Most investors don’t really spend a long time learning information from a different perspective which may or may not be correct.
Whit that in mind, many Investors learn how money flows in the Film industry from the filmmakers they invest in. Apart from the conflicts of interest, there’s another rather large problem with that strategy.
2. FILM SCHOOLS DON’T TEACH BUSINESS AS WELL AS THEY NEED TO
Film Schools can be great at teaching you how to make a film, but they’re generally not good at teaching necessary business skills. Even things as basic as general marketing principles, how best to finance a film, or how to make money with a film under current market conditions.
While film and media are an artistic industry, focusing solely on the quality of the film is not going to recoup the investor’s money. Film Schools aren’t great at teaching branding filmmakers how to define their core demographic, or how to access them once they have.
3. DISTRIBUTION ISN'T WHAT IT USED TO BE.
The big risk in film distribution used to be the gatekeepers. You had to make a good enough film to attract a distributor so you could get your film out there. However, that problem has been traded for an entirely different one, oversaturation of content. I would argue that a new problem is harder to overcome.
The old model was that the home video sales would be able to make a genre film profitable, even if it wasn’t that good. Essentially, if you had access to a wide-scale VHS or DVD replicator, you could make a mint selling the licenses. There wasn’t much competition, so a cottage industry sprung up around film markets.
That model worked when it was much more expensive to make a film. Given the high barrier to entry from needing to raise enough money to shoot on film, as well as develop the skills to expose it correctly, there was relatively little competition compared to the demand. However, now that anyone can make a film with an iPhone and 500 bucks the marketplace has been flooded.
Additionally, since the DVD Market has all but dried up, it’s difficult to make a return for newer filmmakers. VOD (Video On Demand) Numbers haven’t risen to the occasion, since most people can get their fix from watching Netflix. It used to be easy to sell DVDs as an impulse buy at the checkout line. Now that everyone has hundreds of free movies at their fingertips, Why should they pay 3 bucks to watch something when there’s an adequate alternative I can get for free?
So the problem is now less how to get distribution, and more how to market the film once you’ve got it. It’s both hard and expensive to market a film. Generally, it’s best to create something of a hybrid between these two types of Distribution. However, there are issues with that as well, and these are less associated with expertise.
4. SEVERE LACK OF TRANSPARENCY IN INDEPENDENT FILM
I’ve written before about the lack of transparency in Distribution, so I won’t go into too much detail here. In Essence, the black box that is the world of film distribution is very intimidating to many investors. Investors want to be able to know when their money is coming back, and many filmmakers are unable to make any real promises about that. However, there’s another issue with transparency from an investor’s perspective.
Unfortunately, many filmmakers don’t communicate well with their investors or other stakeholders. I’ve spoken with many film commissioners, investors, and others about their frustrations with filmmakers not keeping them in the loop.
Filmmakers understandably focus on the admittedly difficult task of making the film happen. Between all of the tasks like scheduling and budgeting the film, finding the locations, confirming the crew, making the shotlist and storyboards, sending out call sheets, and a whole lot more, it’s easy to let communication fall by the wayside.
5. INVESTORS LAST TO BE PAID
Now I know that Filmmakers are reading this thinking “BUT I GET PAID AFTER THEY GET 120% BACK!?!?” To a level, you’re right. However, unless you waived your producer’s fees, you got paid before they did. Sure, you did a lot of work for often too little money to make your film happen, but you did get a fee to produce this film. If your investor wanted to be cynical about it, you produced or directed a movie for hire that you got to take most of the credit for.
Here’s what a waterfall for a film normally looks like. Investors generally did a lot of work to get their money, and now they’ve paid you to make a film and it’s unlikely they’ll ever get all of their money back.
1.Buyer Fees
2.Sales Agent Commission
3.Sales Agent Expenses
4.SAG/Union Residuals
5.Producers Rep (If Applicable.)
6.Production Company
7.Gap Debt (+Interest)
8.Backed Debt (+Interest)
9.Equity Investor
I may be persuaded to do a financial analysis of what that would actually look like in terms of money. Oh look, I did a blog explaining exactly what this means. Click here to read it.
6.LACK OF ACCESS TO TASTEMAKERS AND CURATION
We explored the numbers of why indexed film slates just don’t work in part two. However it takes a fair amount of training, experience, and a bit of luck to recognize what films will hit and what films won’t. While William Goldman is famous for saying “nobody knows anything,” there has to be a balance between a dart board with script titles and industry experts guiding the ship.
Developing an eye for what makes a successful film is something that most prospective film investors don’t want to take the time to learn, especially since many get burned on their first investment. it takes a lot of time to understand what projects have what fit in the market, and that’s generally not something that an investor has time for.
Having a few sets of experienced eyes looking over what investments would be good to fund is something that could make independent film a more sustainable asset class, and not enough investors have access to it to avoid getting burned.
So, what is there to be done about it? Check the next post for the final installment, How do you make a sustainable asset class out of film?
Also, if you like this content you can get a lot more of it through my mailing list. You’ll also get a FREE film business resource package that includes an investment deck template, contact tracking templates, money-saving resources, a free e-book, and a whole lot more. Again, totally free. Get it below.
Click the tags below for more articles on similar topics.
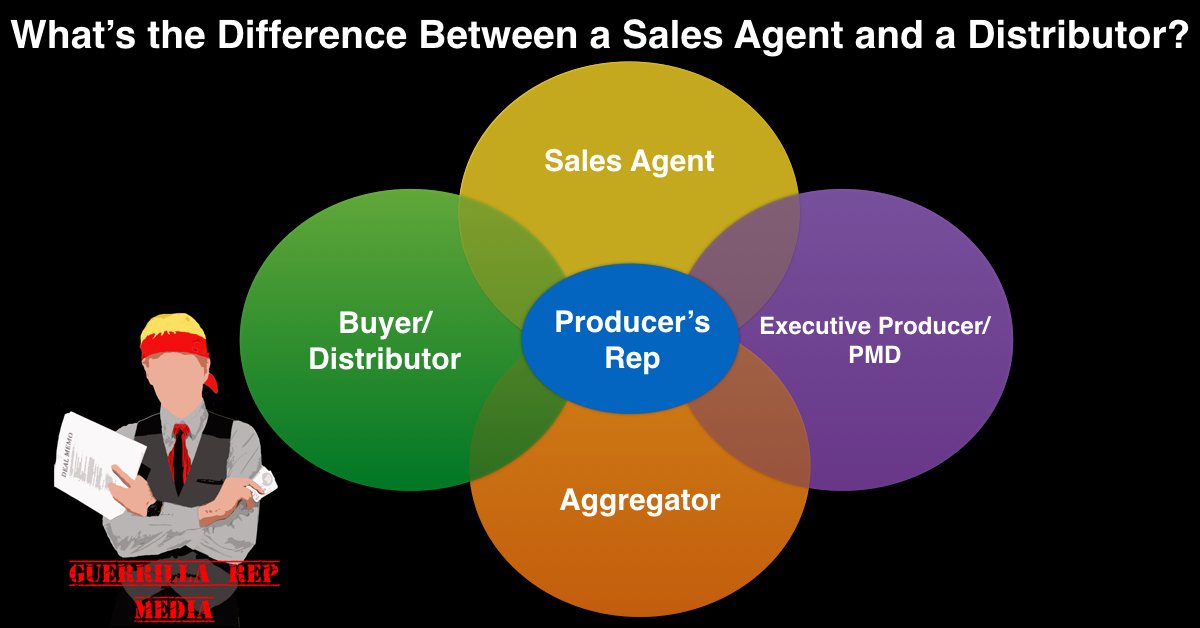
What’s the Difference between a Sales Agent and Distributor?
Too few filmmakers understand distribution. Even something as basic as the disfference between each industry stakeholder is often lost in translation. This blog is a great place to start
As a Producer’s Rep, one of the questions I get asked the most is what exactly do I do? The term is somewhat ubiquitous and often mean different things to different people. So I thought it might be a good idea to settle the matter. In this post, I’ll outline what a producer’s rep is, and how we interact with sales agents, investors, filmmakers, and direct distribution channels. But first, we need a little background on some of the terms we’ll be using, and what they mean. These terms vary a bit depending on who you ask, but this is what I’ve been able to gather.
Would you rather watch/listen than read? Here’s a video on the same subject from my Youtube Channel.
Like and Subscribe! ;)
DISTRIBUTOR / BUYER
A distributor is someone who takes the product to an end user. This can be anything a buyer for a theater chain, a PayTV channel, a VOD platform, to an entertainment media buyer for a large retail chain like Wal-Mart, Target, or Best Buy. The rights Distributors take are generally broken up both by media type and by territory.
For Instance, if you were to sell a film to someone like Starz, they would likely take at least the US PayTV and SVOD rights, so that it could stream on premium television and their own app which appears on other SVOD services like Amazon Prime, or Hulu. They make take additional territories as well.
Conversely, it’s not uncommon to sell all of France or Germany in one go. It should are often sold by the language, so sometimes French Canada will sell with France. This is less common as of late.
Generally, these entities will pay real money via a wire transfer, and almost deal directly only with a sales agent. Although sometimes to a producer’s rep, and VOD platforms will generally deal with an aggregator. The traditional model of film finance is built around presales to these sorts of entities, but that presale model has recently shifted.
Recently, more sales agents have begun distributing in their territory of origin. XYZ is a good example of this. Some distributors have branched out into international sales. This is something that we did while I was at the Helm of Mutiny Pictures, to allow us to deal with filmmakers directly in a more comprehensive way.
Sales Agents
A Sales agent is a person or company with deep connections in the world of international sales. They specialize in segmenting and selling rights to individual territories. Often, they will be distributors themselves within their country of origin. This business is entirely relationship based, and the sales agents who have been around a while have very long-term business relationships with buyers all around the world. That’s why they travel to all of the major film markets.
Examples on the medium-large end would be Magnolia Pictures international, Tri-Coast Entertainment, and Multivissionaire. WonderPhil is up and coming as well, as is OneTwoThree Media. Lionsgate and Focus Features would also be considered distributors/sales agents, but they’re very hard to approach. They also both focus on Distribution over sales.
Generally, these sales specialists will work on commission. They may offer a minimum guarantee when you sign the film but that is not common unless you have names in your movie. Generally, they will charge recoupable expenses which mean you won’t see any money until after they’re recouped a certain amount. In general, these expenses will range between 10k and 30k, with the bulk falling between 20 and 25k. If it’s higher than 30k without a substantial screen guarantee, you should probably find another sales agent. There are ways around this, but I’ll have to touch on this in a later blog [or book].
A sales agent commission will be between 20% and 35%, this is variable depending on several factors, but generally 25% or under is generally good, and over 30% is a sign you should read more into this sales agent. Lately, this has been trending towards 20% with a slight uptick in expenses.
Aggregators
Aggregators are companies that help you get on VOD platforms. The most important service they provide is helping you conform to technical specifications required by various VOD platforms. This job is not as easy as you would think it is, which is why they charge so much. Additionally, they have better access to some VOD platforms than others. These days, it’s very difficult to get on iTunes or most platforms other than Amazon’s Transactional section without one.
Generally, aggregators charge a not insubstantial fee to get you on these platforms, and they offer little to help you market the project. Companies like this include Bitmax and arguably filmhub or IndieRights.
There are merits to going this this route, but they can be expensive, often costing about one thousand USD upfront and growing from there. If they operate on a commission like Filmhub or Indierights, they won’t help you with marketing so you’ll have to spend a decent amount there in order to get your film seen.
Producer of Marketing & Distribution (PMD)
In the words of Former ICM agent Jim Jeramanok, PMDs are worth their weight in gold. A PMD is a producer who helps you develop your marketing and social media strategy, your Festival strategy, and your distribution strategy. They’re also quite likely to have some connections in distribution. They’re there to give your film the best possible chance at making money when it’s done.
Generally, they’re paid just as any other producer would be, but if they’re good, they’re worth every penny. With a good PMD on board, your project’s chances for monetary success are exponentially better.
If you’re an investor reading this, you want any film you invest in to at least have access to a PMD or Producer’s Rep, if not a preferred sales agent or at least domestic distribution. (Not Financial Advice)
Executive Producer (EP)
In the independent film world, these are producers who are hyper-focused on the business of independent film. They either help raise money to make the film, or they help bring money back to those who put money into it in the first place. As such, the traditional definition in of an indiefilm executive producer is someone who helps you package projects by attaching, bankable talent, investors, or other forms of financing. They’ll also help you design a beneficial financial mix, [I.E. where can you best utilize tax incentives, presales, brand integration, and equity, and gap debt.] in order to help your project have the best chance of success. They can also play a significant role in distribution. The latter is where most of my EP credits come from.
Often, they’ll take a percentage of what they raise or what they bring in. sometimes they’ll require a retainer, but most of the time they should have some degree of deliverables such as business plans, decks, or similar as part of that. These fees should not be huge, but they will be enough to give you pause due to the amount of specialized work involved in doing these jobs.
Producer’s Reps
I’ll go into this much more deeply next week, But Producer’s Reps are essentially a connector between all of these sorts of people and companies. Producer’s Reps will connect you do sales agents, aggregators, buyers, and investors. But more than that, a good one will help you figure out how and when to contact each one. Most often, they’re credited as an executive producer or a consulting producer as the PGA does not have a separate title that applies to this particular skillset. For a more detailed analysis of what exactly a Producer's Rep does, Check out THIS BLOG!
Thank you so much for reading! If you found it useful, please share it to your social media or with your friends IRL. If you want more content like this in your inbox segmented by month, you should sign up for my resources pack. I send out blog digests covering the categories and tags on this site once per month. You’ll also get a free EBook of The entrepreneurial producer with this blog and 20 other articles in it, as well as templates, form letters, and money-saving resources for busy producers.
If this all seems like a lot, and you need your own personal docent to guide you through the process, check out the Guerrilla Rep Media Services page. If you’d rather just get a map or an audio tour and explore the industry on your own, the products page might have some useful books or courses for you. Finally, if you just appreciate the content and want to support it, check out my Patreon and substack.
Peruse the tags below for related free content!
One Simple Tool to Reopen Talks with Investors
Closing an investment is not the same thing as finding an investor. Here’s a very valuable tool for closing an investor you thought was lost.
Man in suit in front of a chalkboard with angel wings drawn on it holding fanned out 100 dollar bills in front of his face.
Taking a little bit of a break from the visions of the film industry and the direction that it should go in, this week I'll be offering a piece of useful advice for all the producers out there. I should start this by saying that I am NOT a financial planner. I am IN NO WAY qualified to evaluate security. I am also not qualified to give professional advice as to what stocks to buy, how to manage a portfolio, or anything even remotely related to that information.
In my time at the Institute for International Film Finance and Global Film Ventures, I’ve heard many people speak on various tricks to get Films Financed. One of the single most valuable tools in my arsenal is one that I will share with you now. I will say this was not developed by me, but rather by a speaker for one of my events a while back. I will start by saying that in order to be a producer, you need to understand your competition. Not just in terms of other movies and entertainment that are up against yours in the marketplace, but also how your investment stacks up against other potential investments that High Net Worth Individuals may be considering. This requires that a savvy producer understand the stock market, as it is the most common place where investors keep their money.
It’s important to understand that just because someone is worth 7 or 8 figures doesn’t mean they have millions of dollars to throw around. Most of their money is “Tied Up.” Pretty much any qualified Investor you’ll talk to will have a rather large stock portfolio. A lot of their stocks they’ll have been holding for quite a long time, and they’ll have grown quite a lot in value in the time they will have held them. Given the amount of Capitol Gains Tax they’d have to pay on selling those stocks, getting them the liquidity needed to invest in your film can be a difficult sell.
If you’re talking to a wealthy friend or relative, and they’re interested in your project, the little voice in their head is likely saying things along the lines of, “Hmm… I like it, it’s got potential, but I’d have to sell this, this and this, and my capital gains tax would be this…” That alone is often enough for them to not invest, sometimes simply out of the hassle and paperwork involved in the transaction, not to mention the loss of money. That, my dear readers, is where portfolio loans come in. A Portfolio Loan is essentially a mortgage on a stock portfolio. It allows the investor to keep the stocks in their portfolio, but also free up some money to invest in other projects, such as yours.
It’s extremely low interest, often below 4%. The interest varies week to week, so for precise rates have your Investor contact their broker and/or financial planner. It’s lower interest than borrowing on margin, and while there are many risks involved, the repayment terms are very flexible, and the interest can often be offset by stocks that pay dividends. Also, if you’re borrowing on Margin, you are technically only allowed to invest in other stocks, at least according to the SEC. Although that is admittedly not all that well enforced. This tool can be a great excuse to call up some of your potential investors who have all but turned you down, and can help to reopen conversations with them. It has done just that for me, as well as several of my clients.
In no waay should this be considered financial advice, but in my personal experience this tool is best used in times when the market is expected to go up over the period between when your investor funds your project and when you start to pay them back out. That makes it an excellent tool for when we’re heading towards the bottom of a bear market or towards the beginning of a bull market that is expected to continue. In times when the market is pretty much at its peak, it would probably make more sense to just liquidate part of their portfolio in favor of a higher-risk speculative investment such as an independent film.
Again, I’m not a financial planner, advisor, or a lawyer. Contact one of those people if you really want to know more about this, but just knowing what to ask about can be a huge leg up. As always, be well and thanks for reading, and please share this with your friends!
If you want to hear more from an experienced Executive Producer, or find other tips, tools, and templates you should sign up for my free film business resources package. It includes contact tracking templates, form letters, and even a deck template that should translate to your investors better than most look books sign up for that below and follow on social media for all the latest from Ben Yennie and Guerrilla Rep Media
If you liked this content, but need help from an experienced producer to take your project to the next level, check out the services offered by Guerrilla Rep Media by clicking the button below. If you’re the sort who would rather save some money and do it yourself but need a roadmap, check out my books, courses, and other standalone projects. Finally, if you just appreciate this content and want to support it, check out my Substack and Patreon. Those services don’t pay my bills the same way film projects do, but they help justify me creating more content like this.
Check out the tags below for more FREE content.
Why Film Needs Venture Capital
Part of creating a sustainable revolution in the film industry is creating a new system of finance. For that, we should look to other industries starting with Private Equity and Venture Capital. Here’s how we do that.
A lightbulb next to a chart outlining the allocation of venture funds in 2011 above a text blurb outlining the data source.
There’s an old joke that goes something like this. Three artists move to Los Angeles, a Fine Artist, a poet, and a Filmmaker. The first day they’re in town, they check out the Mann’s Chinese Theater. When they get there, a wave of inspiration overtakes them. The fine artist says, “This is incredible, I have to draw something! Does anyone have a piece of chalk?” Low and behold a random passerby happens to have one, and hands it over. The fine artist does a beautiful rendering on the sidewalk.
Watching this, the poet says, “I’ve had a flash of inspiration, I must write! Does anyone have a pen and paper?” It happens to be a friendly sort of Los Angeles day, and someone hands over a pen and paper. He writes a beautiful Shakespearean sonnet about his friend’s artistry with the chalk.
The filmmaker says “This is amazing, I’ve got to make a movie about it! Does anyone have any money?”
Even though the costs of making a film have been cut drastically, the joke remains true. I mentioned in my last post that the film world is in need of new money, and that what the film world really needs is something akin to Venture Capital. I think the topic deserves more exploration than a couple paragraphs in a post about transparency.
Venture capitalists bring far more than money to the table. They also bring connections and a vast knowledge of financial and industry specific business knowledge to the table. Essentially these people are experts at building companies, and when you really break it down the best films really are just companies creating a product.
The contribution of connections and knowledge is just as vital to the success of the startup as the money is. We have something somewhat similar in the film world, it’s generally the job of the executive producer to find the money for the film and put the right people in place to run the production and complete the product.
The biggest problem is that good executive producers with contact to money are few and far between, and there are very few connection points between the big money hubs and the independent film world. Filmmakers often don’t only need money, they need to have an understanding of distribution and finance that many simply do not have, and most film schools just do not teach. These positions are generally not full time positions, and most filmmakers just don’t have the money they need to pay people like this. If a venture capital model were to be adapted in film, the firm could link to these experts, and included in the budget for the film at a cost far less than it would normally be, because the person could split their time between all of the projects represented by the firm.
Most people understand that filmmakers need money, what many people do not understand is that there are very valid reasons for an investor to invest in film.A good investor knows that a diverse portfolio is far better than one that focuses solely on one industry. Industries can change and the revenue brought in by any single industry can crash with little notice. Savvy investors will seek to have money in many pots as it really helps to weather through downturns. Film is considered to be a mature industry, and has grown steadily over the past several years, even in the economic downturn. In fact, the film industry is moderately reversely dependent on the economy, so it often does better in economic downturns.
The biggest problem is that most investors just don’t invest in things they don’t know. Investors need to understand an investment before they put money into it.
Film is a highly specialized and inherently risky business. All the money goes away before any comes back, and that can scare off many investors. Especially since they often don’t understand what a good use of resources for a film is and are often incapable of seeing when the project should be stop-lossed as to not lose any more money.
One solution a venture capital firm could bring to this industry that single investors simply cannot is stage financing. Stage financing is a system of finance that is widely used in Silicon Valley. The concept is basically that the investors only release funds once certain checkpoints are met. Single angel investors do not have the time or expertise to act in this way, which is a big part of the reason for the standard escrow model. If a project that makes it through the screening process is only given the money they need for pre production up front, they must pass a review to have funds released for principle photography then it becomes a far more sustainable investment.
Filmmakers may balk at the idea of review, but quite frankly so long as the production is being well managed, they should be able to complete the checkpoints and have the additional funds released with little difficulty, assuming that the right review panel is put in place. The fund itself has every reason to see it’s projects through to completion, so it will only be filmmakers who are not doing their jobs that end up not passing the review process.
Edit: Additionally, there are deals that can be made to help agents and bankable talent feel more comfortable with such a process. This may be a subject of a later blog, and is mentioned in the comments.
Why does the fund have every reason to see films through to completion? Because if the films are not completed, then the fund will have lost all the money it put in with no chance of getting it back. That said, if the production is a disaster, and it’s clear that additional funds would not actually result in a finished and marketable film, then it is far better to cut losses and move on with other projects that have higher potential for revenue.
As mentioned in the last blog, a lack of transparent accounting is also a big issue with investors.
A single filmmaker does not really have the ability to negotiate with a distributor, at least not to a level necessary to resolve the transparency issue. In the relationship, the distributor has all of the power and there’s really very little most filmmakers, especially those just starting out, can do to change that.
But in film as in any industry, money talks. If there were a venture capital firm for film that only worked with distributors who have transparent books, and those distributors could then turn around and propose new projects to the venture capital firm, then some of the issues of transparent accounting could start to change. Many distributors, especially those working in the low budget sphere, are continually raising money for their own projects. So, having a good relationship with a venture capital firm is a big incentive to maintain good books and responsible business practices for filmmakers.
It got listed in the comments section of Black Box that filmmakers shouldn’t necessarily need to have that much business sense, since it takes their whole being to create. Filmmaking is indeed a collaborative effort, and it’s not a director’s job to think about target demographics and marketing strategies. The problem is the people in the film world that truly understand investment and recoupment are few and far between. Many of them also take advantage of filmmakers, as evidenced by the stories of studio accounting from Black Box. Part of what’s needed is the creation of teams that have what it takes to both tell quality stories with high production values, also get the films to market and figure out exit strategies, target demographics, and general budget recoupment tactics.
Many Film Schools just don’t teach this part of the business. Film schools focus everything on how you can make the film, and what it takes to do it, but few of them really give you the ability to actually go raise money. So what’s really needed is a new class of producer that understands the executive side. What’s really needed is a new class of investor that understands what it takes to invest in film, the risks, the rewards, and how it’s diversified. What’s really needed in film is a company that can successfully link the two together, and create a new class of media entrepreneur. What’s really needed is an incubator for independent film with a team that can execute both of these aspects and create a sustainable business model out of it.
Right now no such organization really exists. Legion M has some elements of it, but they miss the new talent discovery elements in favor of risk abatement. Slated works similar to AngelList, but I’m not sure their track record is what it needs to be to justify their price point. I’ve been trying to start one between my various projects with angel groups, Mutiny Pictures, Producer Foundry, and other ventures. It’s clear that the industry is changing, but quite frankly it needs to. The best way to effect the change in practices that need to happen in the industry is to change the way the industry is financed. The entrance of a film fund that operates on principles more akin to the aspiraations of a venture capital firm would do just that, and is exactly why it needs to happen.
If you enjoyed this blog, please share it to your social media. You should also join my mailing list for some curated monthly blog digests built around categories like financing, investment, distribution, marketing, and more. As well as some templates (including a deck template) as well as other discounts, templates, and other resources.
Check out the content tags below for related content
Black Box - a Call for Transparency in Film
The concept that Film Distributors aren’t telling you the whole truth isn’t unknown. However, the problem is deeper than you may realize. Here’s why.
A Black cube on grass in a yard, with the Title “Black Box” in the upper left corner and the subtitle “An In Depth Analysis of ‘Hollywood accounting” in the lower right corner, and logos for Guerrilla Rep media and PRoducer Foundry in the lower left corner.
Photo Credit thierry ehrmann Via Flickr, Modifications made to add title, subtitle, and logos
The process of Filmmaking has been evolving rapidly over the past decade. With the massive change in the availability of equipment, negating the need for tapes or stock, and bringing the professional quality down to a price point thought unfathomable merely a decade ago, the barrier to entry for making a film has been almost completely obliterated. Additionally, education on how to make a film has become widely available, from the massive emergence of film schools to a plethora of information available in special edition DVDs, anyone can learn how to make a film. However, the same cannot be said for Film Distribution. Film distribution is still a black box from where no light or information emerges. There is a very palpable air of secrecy around film distribution, and now that film production has become available for anyone curious enough to seek it, it’s time the same is done for film distribution.
I’ve always loved movies, and I’ve been making films in some fashion for nearly a decade. Even though that’s really not that long, I realized that when I started, camcorders were still fairly rare among middle-class families, and far rarer among high school students. Even the local Access channel worked with three-chip cameras, and those who could afford it swore by the film. That landscape is now nearly unrecognizable, now every other high school freshman carries a 1080p camera in their back pocket anywhere they go. This process has been going on for decades, far longer than my personal experience.
In the 70s, even Super 8 home movies were few and far between. To make a movie in the 70s involved an incredible amount of time, effort, and skill. Many learned by trial and error, with limited training and education often in the form of watching the great films of their eras. In those days, no one went to Film School, because there really weren’t that many of them. You pretty much had to go to New York or LA.
Even those who entered the industry in the 60s and ’70s often went to school for something else. Today, there are 389 Film Schools spread across 43 states, which considerably changes the landscape for Education.
However the same cannot be said for film distribution. Despite the fact that technology has evolved beyond what even the most visionary filmmakers could scarcely imagine back in the 70s. Much of it is still a black box where even the most simple information about budgets and returns are kept largely under lock and key. Studio accounting and net proceeds are just as secret now as they have been since Jimmy Stewart became the first Actor to be a net profit participant back in the 50s.
Even if you made a film that’s being represented by a distributor, many of them will not share accurate information regarding the returns you’ve made. A simple balance sheet is difficult to track down, and even if you can get one it’s often hindered by studio accounting, and the breakeven point is never reached, so the filmmaker never sees his or her share in the net proceeds, also known as profit participation. If filmmakers don’t make money making films, then all they have is an expensive hobby that is unsustainable in the long term. The problem is so vast that even Star Wars Episode 6 never made a profit. Even if they can get their first project bankrolled, unless they can make a profit on their film it is unlikely that they will get to make another one. In the independent film world, most times if the producer never sees their share in the net proceeds, then neither does the investor who footed the bill.
If the investor doesn’t see profit, then they won’t be an investor for long. Unlike the filmmaker, most of them won’t continue to do this just for the vision. The first thing any savvy investor will tell you is that they only invest in what they know. And while they may now be easily able to find information on the process of making the film, the metrics measuring the performance of independent films are unclear and almost always unreliable. If an investor can’t decode and project revenue through clearly definable analytics, most of them are far less likely to close an investment deal. Even if they do invest, if they feel like the distributor is not telling them the whole story, they generally won’t invest again.
If the Industry is to change, new money to enter it. The old money is tied up in sequel after sequel, and rehashes of old stories. The movie-going public is fed up with it and want something new, different from the old franchises. This leaves a demand in the industry for quality content that is simply not being filled to the extent it needs to be. In a way it’s similar to the ’60s and early ’70s here in San Francisco when Venture Capital was just starting, there are many talented young people with great ideas, but little business sense.
The studios are entrenched in the old ways of thinking, and behemoth companies don’t adapt well to change. Startups do adapt well to change, and they really can change thought processes through ideas that take hold. The Film Industry is changing more rapidly than ever before, it will likely be just as unrecognizable in another 5 years as it was 10 years ago. Anyone can make a movie, even with a small device they carry in their pocket. The old companies and the old money can’t adapt as quickly as things are changing, so logically we need new ideas and new money to enter the industry and shake things up.
This is exactly the effect that Venture Capital had when the Traitorous Eight left Shockley Semiconductor to start Fairchild, and then left to start other companies that eventually became Silicon Valley. Fairchild was only able to be started due to a new idea that evolved into what is now known as Venture Capital. In order to effect change as quickly as is needed, something similar must happen in the film industry. But Venture Capital can’t enter an industry where the risks are incalculable. Without a more transparent method of accounting, the risks are indeed incalculable.
The industry is evolving more rapidly than ever before. The future is unclear. It’s a wide-open frontier where anyone can make a movie, even with a small device they carry in their pocket. The process of film production has moved out from the dark rooms and light-proof magazines of old and exposed for all to see. It is time for the business side to do the same. It is time for every filmmaker and investor to have a clear understanding of Distribution. It is time for daylight to expose the studios’ accounting practices. It is time for transparent accounting in film.
While there's not a lot an individual can do about the lack of transparency in the film industry as a whole, there are ways that we as individuals can band together to have an impact. Those tactics are some of what I tried to implement at Mutiny Pictures, and what I address in my content, groups, and consulting. One of the goals of porting over my website was to greatly lessen advertising and sales, but check the links below to learn more about ways you can impact not only your career but the industry as a whole. More details on each of the buttons found below.